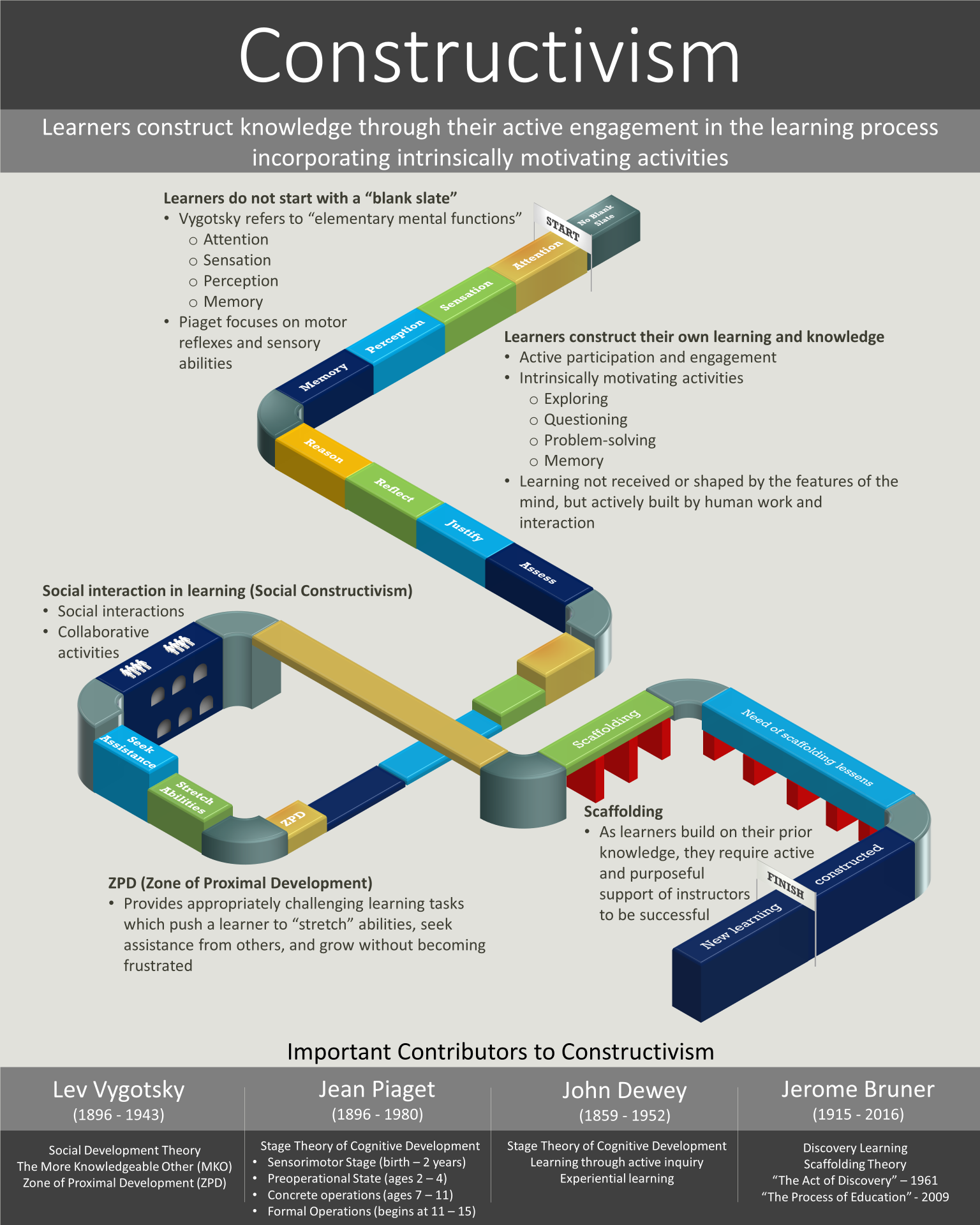
LEARNING SCENARIO
Foundational learning scenario from week 2 (Behaviorism)
A parent wishes her young child to memorize a short poem. Each evening before bed, the parent sings the poem to the child before bed to an already familiar tune which the child enjoys. The child smiles each time the parent sings the poem, not because of the words of the poem, but because the child already loves the tune that the parent has added to it. After a few days of this nightly repetition, the parent beings to sing the poem also at times during the day that they are playing together, dancing, and just having fun. Soon, when the child hears the parent singing the poem, the child assumes it is time to dance and play. But when the child is misbehaving, the parent refuses to sing the poem, and as punishment, will not allow the child to sing the poem either. The child soon begins to associate the poem with the tune, dancing, and other fun times. After a short time, the child begins to sing the poem by herself without the parent any time she is playing and having fun. By singing it repeatedly by herself when she is playing and having fun, she is showing the behavior that she has memorized the poem.
Constructivism theory applied to create additional learning that complements or adds to the initial behaviorist scenario.
Through the help of the scenario mentioned above, the child's love of music and singing has grown. She has also memorized the simple tune which contains the poem. The parent plays the tune on a Glockenspiel while singing it for the child. The child wants to try to play it, seeing her mother playing the tune. The child is able to learn to play the first few notes but not the rest of the tune. By singing the song to herself, the child learns to play more of the song on the Glockenspiel but is not able to play the entire song. The mother holds the child's hand and leads her to hit the correct keys as they sing the song together. After the child seems to be leading the mother's hands in playing the song, the mother lets go but continues to sing and point to the correct keys. After the child progresses further, the mother stops pointing at the keys but continues to sing to help guide the child. In the end, the mother can stop all assistance as the child can now sing and play the tune on the Glockenspiel by herself.
Describe specifically what you believe would be the skills in the Zone of Proximal Development (based on the learners in your scenario).
The mother is assisting the child in playing the song on the Glockenspiel. As the child has previously learned the tune, she can use that knowledge to help her differentiate between correct and incorrect notes while learning to play the tune on a Glockenspiel.
Discuss at least one scaffolding strategy and one social constructivist strategy you could use to help learners take an active role in constructing their own knowledge.
Scaffolding Strategy - Assess Prior Knowledge or real-life examples related to the topic
This strategy helps students to understand ideas that can, in themselves, be hard to grasp. For example, when discussing the benefits of good customer service, ask students to share experiences of poor retail customer experience. After the examples are shared, ask what made the service poor, and what was the effect on the student as a customer.
Social Constructivist Strategy - Small group projects
This strategy helps students to learn through social interaction and collaborative activities. I have benefited from this strategy often in the workplace and in our learning environment.
References
Giesen, J. (n.d.). Constructivism: A Holistic Approach to Teaching and Learning. Retrieved from https://niu.edu/facdev/_pdf/constructivism.pdf
McLeod, S. (2018). Lev Vygotsky. Retrieved from SimplePsychology: https://www.simplypsychology.org/vygotsky.html
van de Pol, J., Monique, V., & Jos, B. (2010). Scaffolding in Teacher-Student Interaction: A Decade of Research. Educational Psychology Review, 271-296.
Thirteen Ed Online (2004). Constructivism as a paradigm for teaching and learning. https://www.thirteen.org/edonline/concept2class/constructivism/index.html
